Java StringBuffer deleteCharAt() Method
In Java, the deleteCharAt() method of the StringBuffer class is used to delete the character at a specified index in the string.
Example 1: The below Java program demonstrates the use of deleteCharAt() to remove a character at a specific index from the string.
// Removing a character at a specific index
class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("Hello, World!");
System.out.println("Original String: " + s);
// Delete character at index 5
s.deleteCharAt(5);
System.out.println("New String: " + s);
}
}
Output
Original String: Hello, World! New String: Hello World!
Note: After deletion, the subsequent characters are shifted left. It’s important to handle index bounds properly to avoid the StringIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Syntax
StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
- Parameter: index - The element you want to delete.
- Return Type: This method returns the modified StringBuffer object with the character removed.
Note: If the index value is negative or an index greater than or equal to the length of the sequence, this methods throws an StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
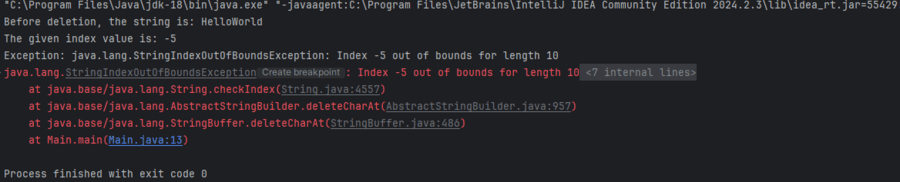
Example 2: The below Java program demonstrates deleting a character at an invalid index throws a StringIndexOutOfBoundsException and handle it with a try-catch block.
// Handling invalid index with exception
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// Create an object of the StringBuffer
StringBuffer sb
= new StringBuffer("HelloWorld");
System.out.println(
"Before deletion, the string is: " + sb);
// Initialize the index value
int i = -5; // Invalid negative index
System.out.println("The given index value is: "
+ i);
// Using the deleteCharAt() method
System.out.println(
"After deletion, the remaining string is: "
+ sb.deleteCharAt(i));
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
}
}
}
Output: