getfattr command in Linux
The getfattr command in Linux is a powerful utility for retrieving extended attributes of filesystem objects. Extended attributes are metadata associated with files and directories, which can be used to store additional information beyond the standard attributes provided by the filesystem.
In this tutorial, we will explain the getfattr command along with its available options.
Table of Contents
Here is a comprehensive guide to the options available with the getfattr command −
- Understanding getfattr Command
- How to Use getfattr Command in Linux?
- Examples of getfattr Command in Linux
Understanding getfattr Command
Understanding these options can greatly enhance your ability to work with extended attributes in Linux. Whether you're a system administrator or a developer, knowing how to use getfattr effectively can help you manage file system metadata with precision and ease.
The getfattr command in Linux is used to retrieve extended attributes associated with files and directories.
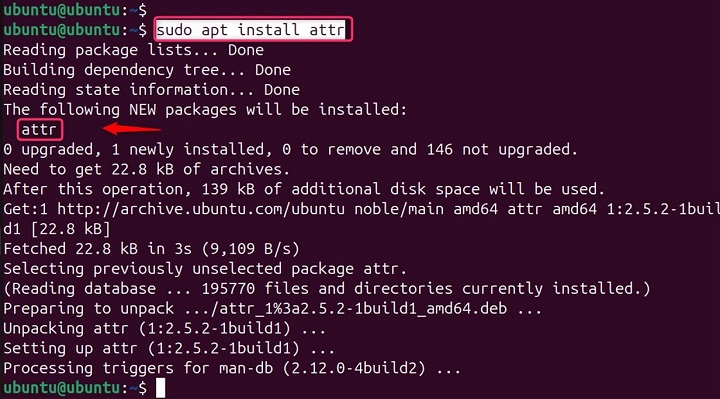
sudo apt install attr
How to Use getfattr Command in Linux?
The getfattr command in Linux provides various options to customize its output and behavior. Here's a breakdown of the available options −
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -n name, --name=name | This option allows you to dump the value of the named extended attribute. It's useful when you know the specific attribute you want to retrieve. |
| -d, --dump | With this option, getfattr dumps the values of all matched extended attributes. It's a quick way to view all extended attributes associated with a file. |
| -e en, --encoding=en | This option specifies the encoding for the attribute values after they are retrieved. The valid encodings are "text", "hex", and "base64". Text strings are enclosed in double quotes, hexadecimal strings are prefixed with 0x, and base64 strings are prefixed with 0s. |
| -h, --no-dereference | Normally, symbolic links are followed to examine the file they point to. This option changes the behavior so that the symbolic link itself is examined. |
| -m pattern, --match=pattern | This option limits the output to attributes that match a specified regular expression pattern. By default, only attributes in the user namespace are included. |
| --absolute-names | By default, leading slash characters are stripped from the output. This option changes the behavior to keep the leading slashes. |
| -P, --physical | Opposite to -L, this option ensures that symbolic links to directories are not followed during a recursive walk. |
| --only-values | This option will output only the values of the extended attributes without encoding them. |
| -R, --recursive | This option tells getfattr to recursively list attributes of all files and directories within a specified directory. |
| -L, --logical | When combined with -R, this option follows symbolic links to directories during the recursive walk. |
| --version | This will print the version of the getfattr utility and exit. |
| --help | Displays help information explaining the command-line options. |
| -x | Specifies the file system type to use. This is necessary if the file system is not automatically recognized. |
| -q | Quiet mode, suppresses output if no extended attributes are found. |
| -v | Verbose output, providing additional details about the extended attributes. |
| -d | Specifies the delimiter to use between extended attribute names and values. |
| -h | Displays the output in a human-readable format, making it easier to understand. |
| -n | Specifies the number of bytes to read for each extended attribute. |
| -e | Specifies the extended attribute name to retrieve. If not specified, all extended attributes are displayed. |
| -c | Specifies the character encoding to use for displaying extended attributes. |
| -f | Specifies the file system's superblock location. This is useful for damaged file systems. |
| -i | Specifies the inode number of the file or directory to examine. |
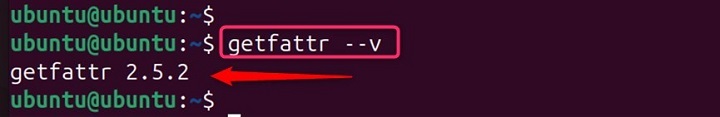
For more detailed information and examples, you can refer to the getfattr manual page. Letâs check its version −
getfattr --v
Basic Usage
Retrieve all extended attributes for a file −
getfattr file.txt

This command will display the extended attributes associated with the specified file.
Examples of getfattr Command in Linux
Here are some practical examples of how to use the getfattr command −
Retrieve the Value of a Specific Attribute
To get the value of a specific extended attribute, you can use the -n option followed by the name of the attribute.
getfattr -n user.comment /path/to/file
Display All Extended Attributes
If you want to list all extended attributes of a file, the -d option will display them.
getfattr -d file.txt

Retrieve Attributes without Dereferencing Symlinks
The -h option tells getfattr not to follow symbolic links.
getfattr -h file.txt

Use Regular Expressions to Match Attributes
With the -m option, you can match attributes using regular expressions.
getfattr -m "^user." /path/to/file
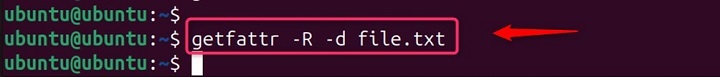
Retrieve Attributes Recursively
The -R option allows you to recursively retrieve attributes from files and directories.
getfattr -R -d file.txt
Encoding the Output
You can use the -e option to retrieve a specific extended attribute by name. Retrieving Specific Extended Attributes −
getfattr -e extended_attribute_name filename
The -e option can be used to encode the attribute values. Valid encodings are text, hex, and base64.
getfattr -e text file.txt

Retrieve a specific extended attribute, use getfattr -e user.comment filename command.
Display Only the Values of Attributes
If you're only interested in the values and not the names of the attributes, you can use the --only-values; option −
getfattr --only-values file.txt

Exclude Leading Slash Characters
By default, getfattr strips leading slash characters from the output. Use --absolute-names to prevent this.
getfattr --absolute-names -d file.txt

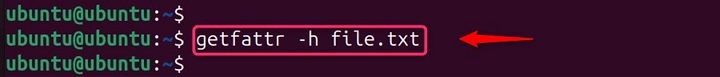
Displaying Extended Attributes in Human-Readable Format
The -h option displays the extended attributes in a more human-readable format, making it easier to understand. Letâs display extended attributes in human-readable format −
getfattr -h file.txt
These examples illustrate the versatility of the getfattr command in handling extended attributes on Linux filesystems.
Retrieve extended attributes for a file on a specific file system
getfattr -x ext4 file.txt

Retrieve extended attributes for a file with a specific inode number
getfattr -i 12345 file.txt

Displaying Extended Attributes for Multiple Files
getfattr file1 file2 file3

By understanding and using the getfattr command, you can effectively retrieve and manage extended attributes associated with files and directories on your Linux system.
getfattr --help

Conclusion
The getfattr command is a powerful utility in Linux that allows users to retrieve the extended attributes of filesystem objects. Extended attributes are metadata components that can be associated with files or directories in a filesystem, providing additional information beyond the standard attributes like file size or modification date.
