instmodsh Command in Linux
The instmodsh command in Linux examines the installed modules on the system. Installed modules are software packages that enhance the capabilities of a programming language, such as Perl.
The instmodsh command is specific to Perl. It provides a simple shell interface to inspect and manage Perl modules installed on your system. It works with Perl's module management system. It is a simple interface to ExtUtils::Installed that lets you inspect installed modules, validate, and even create a tarball of installed modules.
Table of Contents
Here is a comprehensive guide to the options available with the instmodsh command −
- Prerequisites to use instmodsh Command
- Syntax of instmodsh Command
- Examples of instmodsh Command in Linux
Prerequisites to use instmodsh Command
The instmodsh command is primarily used to examine the Perl modules. To use it, ensure Perl is installed on Linux. To view whether Perl is installed or not, use the following command −
perl -v
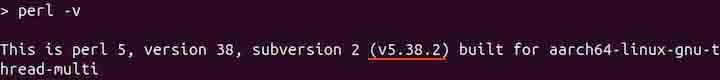
The output from the above command indicates that the Perl is installed. If it is not installed, then install it using the instructions given below −
To install Perl on Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Raspberry Pi OS, Debian, and other Debian-based distributions, use the command given below −
sudo apt install perl
To install it on Fedora, use −
sudo dnf install perl
To install Perl on Arch Linux, use −
sudo pacman -S perl
To install it on CentOS, use the command given below −
sudo yum install perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker
Syntax of instmodsh Command
The syntax of the Linux instmodsh command is as follows −
instmodsh
The instmodsh command requires user interaction. Simply executing the command will list the available subcommands to examine the Perl modules.
Examples of instmodsh Command in Linux
This section demonstrates the usage of the instmodsh command in Linux.
To examine a Perl module from the terminal, execute the instmodsh command −
Instmodsh

It will display subcommands as shown in the above output image. The subcommands and their description are listed below −
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| l | Press l and Enter keys to list the installed modules |
| m [module] | Press m and mention the module name to examine |
| q | To quit the program |
To list the modules, press l and then Return −

The output image shows the installed modules.
To select and examine the module, type m and then specify the name. For example, to select the Digest::HMAC module, use the following command −
m Digest::HMAC

It will display another list of commands −
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| f [all|prog|doc] | To list the installed files of the module by file type all: List all the associated file prog: List the program files doc: List the documentation files |
| d [all|prog|doc] | To list the directories used by the module all: List all the associated directories prog: List the directories containing the program files doc: List the directories containing the documentation files |
| v | To validate the .packlist (It checks the missing files) |
| t [filename] | To create the tar file of the module |
| h | To display the help of the specified module |
| q | To quit the module and return to the instmodsh shell |
To list all the associated files of the selected module, use the f command −
f all
Similarly, to list the associated program files and documentation replace the all option with prog and doc respectively.

To display the associated directories, use the d option with the desired type from all, prog, and doc.
d all

To validate the .packlist, execute the v command. A .packlist file is a special file created during the installation of Perl modules, primarily through CPAN (Comprehensive Perl Archive Network). It serves as a record of the files that were installed as part of the module package.

To create a tar file of the module, run the t command with the file name as an argument −
t modFile.tar

The above command will create a tar file in the current working directory as shown in the following image −

To display the help, run the h command. It will list the same command that appears after selecting the module using m.
To quit the specific module session, use the q command, and to quit the instmodsh shell again use the q command.

Conclusion
The instmodsh command is a handy tool in Linux for examining and managing installed Perl modules. It provides a user-friendly shell interface, allowing users to inspect installed modules, validate their installation status, and even create tarballs.
In this tutorial, we covered several key aspects of using the instmodsh command, including prerequisites for installation, syntax, and practical usage instructions.
